몰입형미디어프로그래밍
- 난 핀란드 사람인데 스웨덴에도 살고 한국에도 살았음. VR/AR에 관심있다.
- AR/VR 프로젝트 과제가 2개 있을거고, 유니티 쓸거임.
- 금요일에는 랩 세션을 진행할거임. 개별 실습 과제와 팀플을 하고, 각종 질문받음.
- 지난주 주제에 대한 실습 과제가 있음. 어렵지 않아요.
- 팀플은 3-4명, 프로젝트는 결과를 발표하고, 코드나 문서 및 시연영상을 제출.
- 왠지 모르겠는데 다들 게임을 만들어요. 시연영상은 진짜 게임 예고편처럼 만들어봐.
- 기말고사가 있을거임.
- 교재는 없고, 강의노트와 녹강, 유니티, C#을 쓸거임.
- AR은 안드로이드 디바이스가 있으면 됨. VR은 학교에 오큘러스와 메타퀘스트2가 있음.
Unity basics
- 유니티는 크로스 플랫폼 게임엔진.
- Game object: scene에 있는 모든 것.
- Mesh: 게임 오브젝트의 모양.
- Colliders: 물체의 물리적 경계. 충돌 판정에 필요.
- Scene: 하나의 게임 화면이며, 여러 게임 오브젝트를 배치할 수 있다.
Unity scripting
- 몰입도: 미디어 경험에서 사용자의 감각이 결합되는 정도.
- Embodiment: 몸에 각종 센서를 부착해서 몰입도를 높이는 것.
- Presensce:
- 좋은 미디어 경험은 사용자가 진짜 가상 세계에 있다고 느끼게 만든다.
- presence는 그런 느낌의 강도. 한국어로 뭐라고 하지…
- 제고 요인: 기술적 품질, 몰입도, 현실성, embodiment, 익숙함, 심미성, 디테일 등.
- 저하 요인: 각종 기술적 문제, 하드웨어의 불편함, 촉감의 부재, 실제 공간의 방해물,
- 80도 이상의 와이드 뷰, 1080p 이상의 해상도, 60Hz 이상의 주사율 등이 필요함.
- Multisensory: 몰입되는 환경을 위해서는 다양한 기술을 결합해 모든 감각을 동원해야.
- 시각: 3D 디스플레이, 돔, HMD, 홀로그램
- 청각: 3D 오디오 효과, 서라운드 사운드
- 촉감: 햅틱 수트, 장갑
- 그 외 후각, 미각도 하드웨어 장비로 가능.
- 몰입형 미디어가 뭐냐?
- 물리 세계의 느낌을 주는 가상 세계를 만들기 위한 시도.
- 몰입형 미디어의 주요 기능: 시뮬레이션, 인간 관계, 심리적 반응, 신체적 반응 등.
- XR(eXtended Reality):
- AR:
- 증강 현실. 가상 콘텐츠를 현실에 놓는다. e.g., 포켓몬 고, 이케아 플레이스 등.
- Augmented virtuality: 증강 가상. AV는 현실의 콘텐츠를 가상으로 가져옴.
- VR: 가상 현실. e.g., 하프라이프 Alyx
- MR: 혼합현실. e.g., 홀로렌즈 AR이랑 뭐가 다른거지? 뒤에 나옴.
Introduction to Augmented Reality
- AR의 역사:
- 1901: 소설 <The Master Key>
- 1968: Ivan Sutherland가 HMD 디바이스 개발.
- 1990: 보잉 엔지니어 Thomas Caudell이 AR 용어를 창안.
- 1992: Louis Rosenberg가 미 공군 연구소에서 첫 AR 시스템을 만들었음.
- 1998: NFL 게임에서 가상의 노란 선을 보여주며 AR이라는 용어를 사용.
- 2000: ARToolKit 릴리즈, 첫 AR 게임 <ARQuake> 출시.
- 2009: ARToolKit이 브라우저를 지원.
- 2014: 구글 글래스 출시.
- 2015: AR 기능을 탑재한 모바일 앱이 대거 출시됨.
- 2016: 포켓몬 고, 마이크로소프트 홀로렌즈.
- 2017: ARKit, ARCore 발표
- 2023: 애플 비전 프로.
- AR의 특성:
- 실제와 가상 세계가 동시에 보여짐.
- 실시간 인터렉션을 제공. 사용자가 가상 콘텐츠와 상호작용.
- 가상 또는 현실 세계의 물체를 정확히 등록할 수 있음.
- AR은 현실을 증강, 개선하는 것을 목표로 한다.
- Mixed Reality(MR):

- MR은 공간 인식을 통해 가상의 콘텐츠를 현실 세계에 올려놓을 수 있다는게 특징.
- 과거에는 AR이 지금처럼 스마트하지 않았어요. AR에서는 가상 콘텐츠가 현실 위에 보일 뿐이었음.
- 사실 지금은 AR이 MR임. 지금은 우리가 AR이라고 부르는게 다 MR이죠.
- AR 디바이스:
- Head-up Display (HUD): 일종의 프로젝터. 시각적으로 보여주는 목적이지, 상호작용은 거의 없음.
- 헤드셋: 두 가지 종류로 나뉨.
- Optical see-through: 유리판 같은 광학 요소를 통해 현실을 봄. e.g., 홀로렌즈, 구글 글래스.
- Video see-through: 카메라를 통해 현실을 봄. e.g., 오큘러스 퀘스트, 애플 비전 프로.
- 모바일/Handheld AR: 스마트폰 같은 포터블 디바이스에서 구현된 AR.
- 공공장소 전광판, 키오스크 등.
- Tracking:
- 현실 세계를 추적하기. AR 시스템이 가상 객체를 현실 세계에 놓아야 하니까.
- Marker-based:
- Fiducial markers: 바코드, QR 코드 기반 인식.
- Image targets: 굵은 윤곽선과 불규칙한 패턴, 고대비 이미지.
- Multi-targets: 전개도를 인식해서 3D 개체로 보여줌.
- Markerless-based:
- 출력된 마커없이 현실 세계를 추적할 수도 있음.
- 더욱 리얼한 AR 경험을 제공. 지원하지 않는 디바이스도 있음.
- Object detection: 3D 개체를 인식.
- SLAM: 현실 환경의 평면을 인식. 가령 테이블 위에 모델을 올리고 싶다면 필요.
- Face tracking: 스노우의 그것. 높은 정확도를 위해 LIDAR 사용할수도.
- Location tracking: GPS나 나침반 활용. AR 내비게이션.
- Anchors:
- 가상 콘텐츠가 어딘가에 고정되어 있지 않다면 카메라를 계속 따라다닐거임.
- 현실 세계의 특정 위치에 콘텐츠를 고정히키기 위해 앵커를 사용할 수 있다.
- 두 가지 중요한 용어:
- World space: 카메라와 가상 개체가 위치한 좌표 공간. 현실 세계에서 위치가 갱신됨.
- Pose: world space에서의 개체 위치와 방향을 표현.
- AR 플랫폼: 애플은 ARKit, 안드로이드는 ARCore, 오픈소스 Holokit 등.
- 좋은 AR 경험을 위한 요인:
- 가상 개체를 현실 세계의 특정 위치에 고정시켜야.
- 사용자의 위치에 따라 가상 개체가 변형될 수 있어야. 가령 가까이 가면 커져야 한다.
- Occlusion: 개체가 다른 개체와 물리적으로 상호작용해야.
- Lighting: 조명을 잘 다루면 현실적.
AR Foundation and AR Project Setup
- 유니티로 XR 개발을 할 수 있음.
- AR Foundation:
- 유니티에서 멀티플랫폼 AR 애플리케이션을 만들게 해주는 툴.
- 디바이스 추적, 평면 인식, 앵커, 얼굴 추적 등 온갖게 다 들어있음.
- iOS에 지원되는 기능이 더 많기는 합니다.
- 유니티에서 AR 프로젝트 만드는 법 설명…
- XROrigin: XR 월드 스페이스의 중심을 표현. 개체의 AR 좌표를 유니티 월드 좌표로 변환.
- XR Simulation: 컴퓨터에서 AR 앱을 테스트해볼 수 있음.
Trackable and Image Tracking
- AR Foundation의 추적 시스템은 현실 세계의 Trackable을 기반으로 동작함.
- 이미지를 인식하고 그에 따른 동작을 프로그래밍할 수 있음.
- 특정 이미지를 인식하고 3D 개체 띄우는 걸 보여줄게:
- 교수님이 라이브 코딩하고 시연하는데 잘 안 됨.
- 30분간 이어지는 눈물의 디버깅쑈… 뭔가 확실히 보여주시려는 듯.
- 실습 수업에서 해결됨. Universal RP 문제였음.
Plane Tracking and AR Raycasting
- AR Plane Manager로 plane을 인식할 수 있음.
- 일단 기본적은 AR scene을 설정하고, XR Session Origin > Add Component > AR Plane Manager 선택.
- hierarchy에 기본 palne을 추가하셈(XR > AR Default Plane)
- 이렇게 하면 인식된 planes를 시각화해서 볼 수 있음.
- 터치했을 때 plane 위에 오브젝트 생성하기:
- 레이를 쏴서 plane 위에 오브젝트를 올릴 수 있다.
- 강의노트 7-8 페이지에 코드가 있음.
- 오늘도 라이브 코딩 하시는 중.
- plane 대신 placement indicator를 쓸 수도 있다.
Building UI with Unity UI (uGUI)
- 유니티로 UI만드는 법을 알려줄거임. 이건 인터넷에 자료가 많으니 짧게 하겠음.
- 모든 UI 요소는 Canvas 컴포넌트를 가진 게임 오브젝트의 자식이어야 한다.
Face Tracking, Light Estimation, Anchors, Occlusion
- 얼굴 추적:
- 얼굴 추적은 AR Face Manager를 쓰면 됨.
- 얼굴에 가상 마스크같은 걸 씌울 수 있다.
- 이건 AR Foundation Remote가 안 됨. 매번 apk를 빌드해야 한다.
- 수정과 빌드를 반복하면서 왜 AR Foundation Remote가 좋은지 보여주고 계심.
- Light estimation:
- Anchors:
- 앵커는 공간상의 특정한 지점.
gameObject.AddComponent<ARAnchor>()같은 식으로 오브젝트에 앵커를 추가할 수 있음.- 공간에 입체 그림을 그리는 예시를 시연하심. 왕신기.
- (잠깐 졸았는데 챕터가 바뀜…)
- XR Interaction Toolkit은 하이레벨 인터랙션 시스템.
- 이 툴킷으로 쉽게 인터랙티브한 AR/VR 경험을 만들 수 있음.
- AR 인터랙션
- AR 제스처 시스템: 손가락 제스처, 탭, 드레그, 트위스트, 핀치 등.
- AR 제스처 interactor and interactables
- VR 인터랙션:
- 크로스플랫폼 XR 컨트롤러 입력.
- 기본적인 오브젝트 호버, 선택, 활성 액션.
- 햅틱 피드백: 컨트롤러 진동
- 비주얼 피드백
- XR 컨트롤러를 이용한 UI 인터랙션
- Handling stationary and room-scale VR experiences.
- 메인 컴포넌트:
- Interactors: gameobjects that can hover, select or activate another gameobject.
- Interactables: gameobjects that the user cnat interact with by tap, drag, press, etc.
- Interaction managers: handle interaction between interactors and interactables.
- Interactor와 Interactable이 Interaction manager를 통해 상호작용한다.
- 스크립트 작성을 안하고 오브젝트와 인터랙션할 수 있음.
- Summary of using AR interactables:
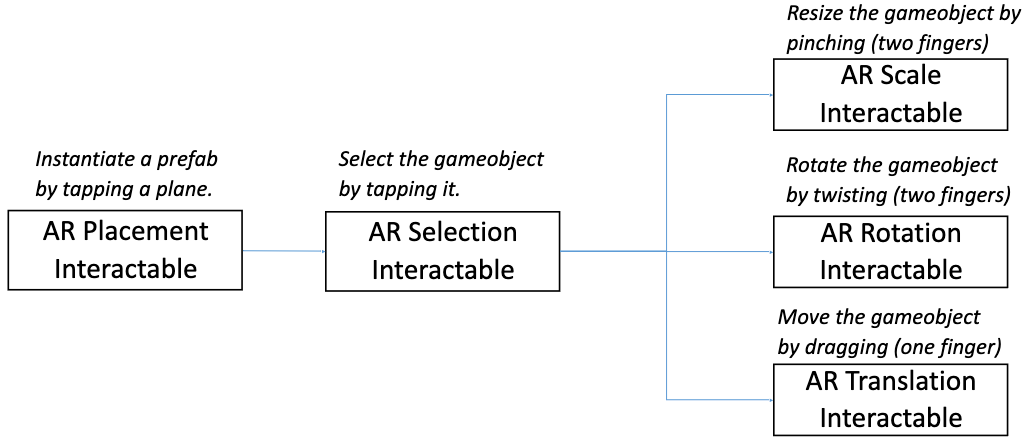
Introduction to Virtual Reality
- VR: computer-generated simulation of a 3D environment, which seems real to the user.
- VR의 목표: generate realistic image, sounds and other sensations that simulate a user’s physical presence in a virtual environment.
- 오늘날 VR HMD(head-moounted display)는:
- 양쪽 눈에 같은 이미지를 보여줌으로써 stereographic 3D scene을 제공함.
- 사용자의 신체나 시선을 추적할 수 있고, 감정을 읽기도.
- Why VR? 현실감을 위해. 훈련, 교육 등 실현하려면 비용이 많이 드는 일을 가상환경으로 해결 가능.
- Stereoscopic VR:
- 우리가 하나의 사물을 볼 때 양쪽 눈에는 살짝 다른 상이 맺힘.
- 살짝 다른 이미지를 양쪽 눈에 보여주면 3D로 보임. 각각의 눈에 렌즈가 하나씩 필요.
- 오래된 방식.
- Monoscopic VR:
- 두 눈에 하나의 거대한 이미지를 보여준다.
- 몰입감은 좀 떨어지지만 저렴함.
- 유튜브에 있는 VR 기능이 이거임. 그냥 2D 이미지가 파노라마처럼 사용자를 둘러싸는 것.
- VR의 역사:
- 1956: Sensorama 발명. 3D 영상과 소리, 냄새와 촉감 제공.
- 1968: 첫 HMD, The Sword of Damocles.
- 1969: Videoplace 발명. HDM를 필요로하지 않는 첫 인터랙티브 VR 시스템.
- 1978: Aspen Movie Map, https://rebeccaallen.com/projects/aspen-movie-map
- 1979: Vital VR 헬멧. 파일럿 시선을 추적하는 군사용 장치.
- 1991: 첫 VR 아케이드 머신.
- 1995: 홈 VR 헤드셋 출시, I-Glasses, VFX1 헤드기어. 혁명적.
- 2010: 오큘러스 리프트의 첫 프로토타입 개발.
- 이후로 구글 카드보드, 삼성 기어 Vr, GloveOne, HTC Vive, Valve Index 등 출시.
- 작년에는 메타 퀘스트 3와 애플 비전 프로가 나왔음.
- VR의 중요한 요소들:
- 3D viewing:
- pincushion effect
- 유니티의 VR 카메라는 uses barrel distortion으로 pincushion effect를 방지.
- Screen resolution: 해상도가 낮으면 screen-door effect가 일어난다.
- 낮은 해상도의 HMD를 위한 기법이 있음: foveated rendering은 시선을 추적해서 사용자가 보고 있는 곳만 고해상도로 렌더링하고, 주변부는 흐리게 함.
- Head, hand, and body tracking:
- VR HMD에는 모션 트래킹을 위한 센서가 있음.
- Positional tracking: 현실 세계의 헤드셋과 컨트롤러의 위치를 추적.
- Hand tracking: 컨트롤러나 장갑, 햅틱 피드백.
- Body tracking: 몸 전체를 추적. 수트같은걸 입음.
- Inside-out vs outside-in tracking:
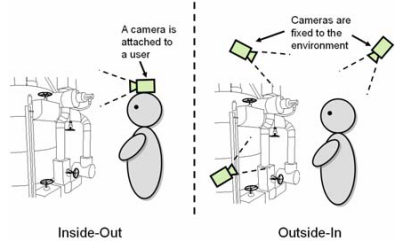
- Inside-Out: 카메라가 사용자에게 달려있음. e.g., Oculus, Meta Quest, …
- Outside-in: 환경에 고정된 카메라가 있고, 사용자를 추적. e.g., HTC Vive, Oculus Rift, …
- 3DoF vs 6DoF:
- 3DoF:
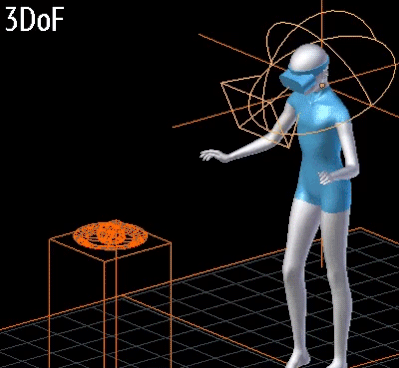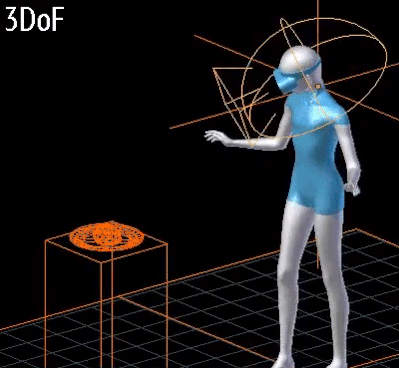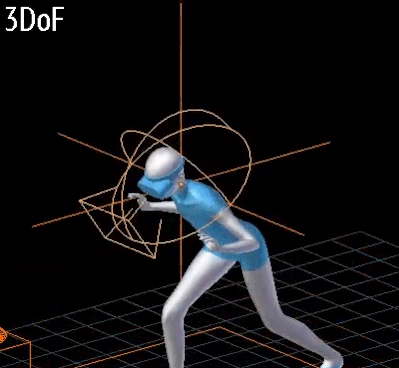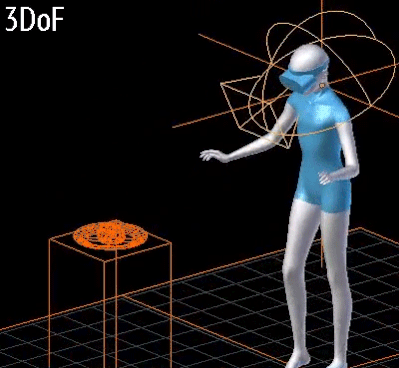
- Rotational movements of the head are tracked (tilt, turn)
- 3개의 회전축.
- 6DoF:
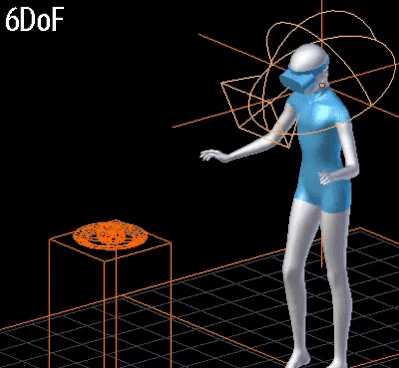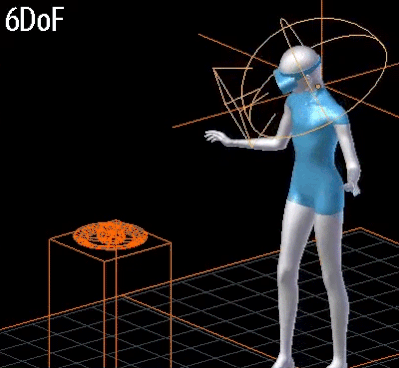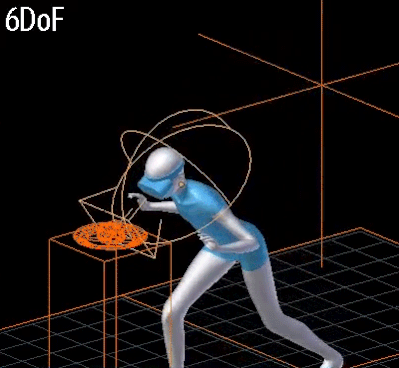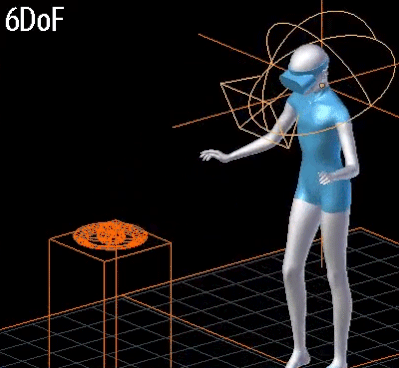
- Rotational movements of the head + position tracking
- 3개의 회전축과 3개의 위치축.
- Embodiment:
- 사용자가 가상의 바디를 자신의 바디라고 느끼는 것.
- first-person VR 경험에 필수적.
- Increased immersion, presence, emotional responses.
- Interactivity:
- Natural: 인터랙션은 자연스러워야 한다.
- Multimodal: 인터랙션은 다양한 입출력을 지원해야 한다.
- High quality content:
- 높은 품질의 콘텐츠는 높은 몰입을 가능하게 만들죠.
- 이 수업은 3D 콘텐츠를 만드는 수업은 아니니까 어셋 스토어에서 가져다 쓰도록.
- Spatial sound
VR Hardware and Software
- HMDs and Projcted VR:
- HMD는 님들이 잘 아는 VR 기기.
- Projected VR은 사방이 스크린인 공간에 사용자가 들어감.
- Types of VR HMD devices:
- Tethered, desktop VR:
- 실제로는 컴퓨터에서 도는데 케이블 통해서 HMD로 전송하는 방식.
- e.g., 플레이스테이션 VR, Steam VR, HTC VIVE, …
- Standalone, mobile VR: 오큘러스, 메타 퀘스트, …
- Hand input devices:
- 컨트롤러나 장갑같은 걸 쓸 수 있음.
- Meta Quest 3나 애플 비전 프로는 맨손도 감지한다.
- Non-hand input devices: Head, Eye, Lip/face, Microphones, Full-body tracking
Types of VR Experience
- Diodrama: 간단한 3D 씬, “Shoebox diodrama”
- First-person experience: e.g., Half-Life Alyx
- Third-person experience
- Stationary vs room-scale VR experiences:
- 둘 다 방에 카메라 설치해두는 건데 뭐가 다른가?
- Stationary: 사용자가 한 장소에 고정. 사용자의 물리적 움직임이 영향을 미치지 않음.
- Room-scale: VR 기기가 사용자의 실제 움직임을 추적해서 가상세계에 반영.
- 3D content creation experiences: VR로 3D 콘텐츠를 만든다. 마인크래프트도 어찌보면…
- Riding/Walking experiences: 롤러코스터 VR은 아주 초기에도 시도한 것. 보통 상호작용이 제한됨.
- 360-Degree media: 비디오인데 360도 촬영해서 몰입감을 선사. 상호작용은 없음.
- Social VR: 아주 유명한 VRChat.
Design Considerations for VR Experiences
- 몰입도 높은 VR 경험을 위한 요구사항:
- 낮은 레이턴시(motion-to-photon): 20ms 미만이어야.
- 높은 프레임 레이트: 90 FPS 이상이어야.
- High resolution
- Wide field of view(FOV): 실제 사람은 220도 정도, 오큘러스 리프트는 90도.
- Precise head/hand/body tracking: 6DoF가 좋겠죠.
- High quality audiovisual content
- Natural interaction
- Blocking of external disturbances
- Simulator sickness:
- VR을 사용하고 멀미를 하는 경우도 흔합니다.
- simulator sickness가 일어나는 다양한 원인이 있음.
- 높은 레이턴시, 낮은 트래킹 정확도: 요즘엔 디바이스가 좋아서 문제가 안 됨.
- Fast acceleration(eye-inner ear mismatch): 등속운동하거나 천천히 움직이도록 해보세요.
- 빠르게 움직일 때 FoV가 너무 넓으면 안 됨.
- 낮은 refresh rate와 flicker, brightness, strong contrast changes.
- 예상치 못한 움직임: 계단을 오르는데 점프가 된다거나… 적이 사용자를 미는 경우.
- Oculus/Meta Quest 2 공식문서 읽고 셋업하셈. 당신 폰과 컴에 관련 앱이 필요함.
- 고성능 GPU가 필요함. 지원이 안 되는 GPU가 있으니 그래픽카드 사양을 잘 보셈.
- 그리고 안타깝지만 윈도우즈 시스템에서만 할 수 있음. (oh no)
- 내일 실습에 오기 전에 미리 설정을 해보렴. 그래야 우리가 도와줄 수 있음.
- 유니티에서 셋업하는 방법을 알려줄게:
- 유니티에서 VR과 Universal 3D 프로젝트는 둘 다 URP를 사용함.
- 난 Universal 3D를 해보겠음.
- VR ㅋ프로젝트 템플릿을 쓰면 샘플 파일들이 들어있어서 좀 지저분하다.
- 패키지 매니저에서 OpenXR Plugin을 설치해라.
- 추가로 XR Device Siulator를 설치하면 기기가 없어도 시뮬레이트할 수 있음.
- 프로젝트 세팅 > XR Plug-in Management > OpenXR > 안드로이드 탭 들어가서 프로파일 추가해라.
- AR 프로젝트에서 메인 카메라 지우고 XR Origin 추가했지? VR 프로젝트도 똑같음.
- 근데 이제 컨트롤러가 있으니까 카메라 오프셋 아래에 있는 컨트롤러를 없앨 필요는 없음.
- 컨트롤러에 XR Interactor Line Visual 컴포넌트를 추가하면 컨트롤러 방향을 선으로 표시해줌.
- 간단한 VR 씬만들고 시연하심. 재밌겠다…🤩
- What is URP?
- 렌더 파이프라인은 씬의 콘텐츠를 스크린에 렌더링함.
- Built-in RP: 모든 플랫폼에서 동작.
- URP: 제한된 성능의 기기에서 동작함. (e.g., 스마트폰, VR 기기)
- HDRP: 고성능 기기에서만 동작함. (e.g., 컴퓨터, 콘솔)
- 상황에 맞게 잘 선택하면 된다.
- What is OpenXR?
- 크로스플랫폼 XR 개발을 위한 표준.
- 유니티 OpenXR 플러그인은 각종 기기에 여러 인터랙션 프로파일을 지원함.
- Hand presence:
- XR Origin에 컨트롤러 외에 Hand, Hand visualizer 오브젝트를 추가하면 손을 인식시킬 수 있음.
- XR Origin에 XR Input Modality Manager 스크립트가 있어야.
- 구현하는 방법은 보강 동영상으로 올려뒀으니 확인해보렴.
Simple Interactable, Locomotion, Ray Interactor, Interaction Groups, and Tunneling Vignette
- XR Simple Interactable
- Locomotion in VR
- Locomotion methods:
- Teleportation: 이동 지점을 선택하면 순간이동.
- Continuous movement: 이동수단 같은 걸 타고 이동.
- Grab move: 뭔가를 잡고 밀고 당기며 이동. (수영하듯)
- Snap/continuous turn
- Climb
- Interaction groups
- teleportation, vinette, grab move 시연하시는 중.
- 플레이어한테는 콜라이더가 없어서 오브젝트를 통과해버림.
- 캐릭터 컨트롤러로 이 문제를 해결해보자.
- URP 설정 건드렸더니 모든 오브젝트가 마젠타가 됨… 머티리얼 RP를 싹 다 스탠다드로 바꿈.
- 스크립트 한줄도 안 짜고 컴포넌트만 추가하고 파라미터 설정해주면 되니까 쉽죠.
- XR Interaction Toolkit은 VR 인터랙션을 쉽게 구현할 수 있게 해줌.

- 총 잡는 예시:
- 권총 모델에 박스 콜라이더 설정해주고… 손으로 잡아보기.
- 앗! 총이 아래를 보고있다. 모델의 Attach transform 위치를 바꿔주자.
- 님들 과제에서 중요한 부분이니까 잘 보셈.
- Interactor hierarchy:

- BaseInteractable을 상속해서 자신만의 인터랙터블을 만들 수 있음.
- UI Interaction: UI를 만들어보아요.
- XR Poke Interactor:
- 인터랙터블과 UI를 터치, 찌를 수 있게 해주는 인터랙터.
- e.g., 대왕 성냥개비로 인터랙터블과 상호작용.
- 오늘은 문 열기 레버 내리기 같은 걸 해볼게요.
- 문 여는건 그냥 hinge joint 컴포넌트 추가하면 됨.
- 시선 추적도 할 수 있어용: eye gaze interactor를 추가하셈.
Notices
- 깜짝 퀴즈 볼거임. 지금 당장.
- 펜과 종이로 20초 안에 질문에 대답해야 함. 이메일로 당신의 정답을 내셈.
- b) FixedUpdate
- d) Layer mask
- (0, 4, 0)
- A frist AR game
- c) Richie’s (?)
- b) Leo (??)
- a) ShanDong (???)
- She’s scream was louder than gunshot. (???)
- April fools’ day…
- lab4 과제가 올라왔는데 arcoreimg.exe 파일이 첨부되어 있음:
- 맥이나 리눅스쓴다면 그냥 AR Core 저장소에서 받아도 됨.
arcoreimg evel-img --input_image_path=<path>하면 이미지 인식률을 체크해볼 수 있음.- 점수가 75점 이상 나와야 마커 이미지로 인식이 잘 된다.
- Q: 데스크탑이랑 모바일 네트워크가 서로 달라서 AR Foundation Remote를 못 씀…
- 중간고사 보고싶은 사람?
- 우린 중간고사 안 봅니다.
- 그러니까 수업 나오셈. 4/22에 나와서 팀플하세요.
- VR 기기 빌려줄게요:
- 팀 1,2,3,4,9는 산621로 오셈. VR 기기랑 USB 케이블을 줄거임.
- 기기는 조심히 써주세요. 엄청 비싸진 않지만 저렴하지도 않음.
- 기기는 항상 박스에 넣어둬라. 케이블도 꼭 챙겨서 나중에 반납해야 됨.
- 케이블이나 충전기가 없는 경우도 있을거임. 그냥 핸드폰 충전기 써보셈.
- 님들 컴퓨터가 안 좋으면 실습실에서 하세요. 실습실 쓸 사람들은 신청서를 제출하렴.
- 6/17 13~15시 산422, 산420에서 기말고사볼거임. 강의실 배정은 TA가 엑셀파일로 올려줄거임.
- 손코딩 없을거임. 그건 실습에서 했으니까.
- 이론적인걸 많이 물어볼거임. 설명하면서 당신이 코드를 제시할 수는 있겠지. 그 코드가 컴파일이 잘 되는지는 노상관임.
- UBILIFE LAB 오세용.
- 6/17 월요일에 VR 기기 반납해라. 상자에 들어있던 거 잘 챙기고. 과제를 일욜까지니까 괜찮지?
- 6/20 금요일까지 당신들 출석이랑 과제 점수 같은 거 최종 점검해라.
About final exam
The final exam scope includes the following lecture notes:
- 03 - Introduction to Immersive Media (slides 2-12)
- 04 - Introduction to AR (slides 5-26, 29-31)
- 05 - AR Foundation and AR project setup (slides 2-7, 13-15)
- 06 - Trackables and Image Tracking (2-13)
- 07 - Plane Tracking and AR Raycasting
- 10 - AR Interaction with XR Interaction Toolkit (slides 2-7)
- 12 - Introduction to VR (slides 2-5, 11-24, 26-40)
- 14 - Simple Interactable, Locomotion, Ray Interactor, Interaction Groups, Tunneling Vignette (slides 1-27)
- 15 - Interaction
Additionally, you should review the sample code related to these lectures. Studying labs 4-7 can also be useful
NOTE: You don’t need to memorize the details of the AR and VR components in Unity Inspector
If you have any questions, please ask
Time and plac
- Date: Monday 6/17
- Time: 1pm~3pm
- Place: Sanhak Hall 422, 42
Instruction
Bring your student ID (or another ID with a photo) because TAs will check your identity
You can bring with you:
- Pencil, pen, eraser, pencil sharpener, ruler, and other necessary accessories for writing your answers.
- English dictionary book (without hand-written notes. We will check!
Q&A
- Q: When can I leave the exam room?
- Q: How long can I be late?
- A: At most 29 mins 59 seconds.
- Q: How do I answer the questions?
- A: write your answers onto the provided answer sheet.
- Q: What kind of questions will there be in the exam?
- A: I haven’t prepared the exam questions yet, but I may mix different types of questions, like:
- multiple-choice questions
- short explanations (e.g. “Explain the following term and give an example.”)
- longer explanations (e.g. "Describe different locomotion techniques in VR and compare them. Explain what XR Interaction Toolkit components you need for each of them. ")
- understanding code (e.g. study code snippets and answer questions about them).
- Q: when I’m finished, what should I do?
- A: make sure that you answered all questions and subquestions and wrote your name on all papers, including the question paper. Then, return the answer sheets AND question paper to the TA.
- Q: Can I go to restroom during the exam?
- A: No. Please go to restroom before the exam.
Memo for final exam
- Immersion is the level of user’s engagement with her/his senses in a media experience.
- Embodiment: ensemble of sensations that arise in conjuction with being inside, having, and controlling a body.
- Important elements for immersion:
- Continuity of surroundings
- Conformance to human vision
- Freedom of movement
- Interaction with the environment
- Narrative engagement
- 3D audio
- Natural social interaction
- Presence means the strength of this feeling:
- Forgetting about the real world
- Losing track of Time
- Reacting to virtual stimuli as if they are real
- Related term: suspension of disbelief
- XR: eXtended Reality
Introduction to AR
- AR aims to enhance real world experiences by using different types of digital congtent.
- Weak AR: imprecise tracking, limited interactivity, …
- Strong AR: accurate tracking, seamless integration with real world, …
- MR: Mixed Reality
- Virtual content can be placed onto the real world through spatial awareness.
- HUD, Headset, Handheld AR, Public space AR, Location-based AR, …
- SLAM(Simultaneous Localization and Mapping) technology analyzes the sensor input of a mobile device and creates points and planes that represent the real world environment.
- Anchors:
- World space: the coordinate space where the camera and the virtual objects are locaated.
- Pose: represents an object’s position and orientation in world space.
- A good AR experience not only tracks the position of the virtual objects, but also changes their transform according to the user’s position.
- Immersive experiences depdend on realistic occlusion and lighting.
AR Foundation and AR Project Setup
- Unity has a plug-in framework called XR SDK that allows XR device manufacturers to integrate their XR libraries into Unity.
- AR Foundation: provides tools to create multi-plataform AR application in Unity.
- XR Origin: represents the center of world space in AR, MR and VR applications.
- AR Session: controls the lifecycle of an AR application.
- Tracked Pose Driver, AR Camera Manager, AR Camera Background
Trackables and Image Tracking
- Trackable: anything in the real world that can be detected and tracked.
- AR Tracked Image Manager: it is used for tracking 2D images.
Plane Tracking and AR Raycasting
- AR Plane Manager creates GameObjects for each detected plane.
- AR Raycast Manager: interacts with the detected planes.
- If you want to raycast against gameobjects that have colliders, use
Physics,raycast() instead.
- XR Interaction Toolkit: high-level interaction system for easy creation of interactive AR/VR experiences.
- Main components:
- Interactors: gameobjects that can hover, select or activate another gameobject.
- Interactables: gameobjects that the user can interact with by tap, drag, press, etc.
- Interaction managers: handle interaction between interactors and interactables.
- XR Interaction Manager: takes care of communication between interactors and interactables.
- Each interactables has three possible states: Hover, Select, Activate.
- There are multiple types of interactors for different types of interactions: Gesture(AR), Ray(VR), Direct(VR), Socket(VR)
Introduction to Virtual Reality
- VR: computer-generated simulation of a 3D environment, which seems real to the user.
- Stereoscopic VR:
- separate views for the left and right eyes, which are slightly offset to create a 3D effect even though the images are 2D.
- VR head-mounted displays are based on stereoscopic images.
- Monoscopic VR: uses the same image for both eyes.
- Important elements of VR:
- 3D viewing:
- pincushion effect
- barrel distortion (ocular distortion correction)
- Screen resolution:
- screen-door effect: fine lines separating the pixels become visible in the displayed image.
- foveated rendering: showing higher-resolution details where the eye is looking at, lower resolution image in the peripheral vision.
- Motion tracking:
- motion tracking: measuring acceleration and rotation on three axes.
- positional tracking: detecting the headset’s and controllers’ positions in the real world.
- inside-out tracking: HMD device has built-in sensors and cameras for tacking the user’s position.
- outside-in tracking: uses external sensors that are set up around the room to track the users.
- 3DoF: rotational movements of the head
- 6DoF: rotational movements of the head + position tracking
- Embodiment
- Interactivity:
- should be natural, so that the interaction can feel more real.
- should be multimodal: so that different input and output modalities can be supported.
- High quality content
- Spatial sound
- Diodrama: a simple 3D scene, which is observed from a third-person perspective.
- First-person experience: the user takes the role of a freely moving agent in the scene.
- Third-person experience: the user watches the scene from a third-person perspective.
- Stationary: the user sits or stands in one place.
- Room-scale: the VR device translates the user’s movement in the real world to the character’s movement in the virtual world.
- Requirements for a high-quality VR experience:
- low latency
- high frame rate
- high resolution
- wide field of view
- precise head/hand/body tracking
- high quality audiovisual content
- natural interaction
- blocking of external disturbances
- Simulator sickness:
- A condition where a person exhibits symptoms similar to motion sickness caused by playing first-person Vr experiences.
- It caused by a mismatch between what eyes and inner ear sense.
- If the player needs to move fast, reduce the field of view: tunneling vignette
Simple Interactable, Locomotion, Ray Interactor, Interaction Groups, and Tunneling Vignette
- Locomotion: moving from one place to another in a virtual scene.
- Physical: motion-based(continuous), roomscale-based(continuous)
- Artificial: controller-based(continuous), teleportation-based(non-continuous)
- Teleportation, Continuous movement, Snap/Continuous turn, Grab move, Climb
- XR Origin(VR): represents the player in VR.
- Interaction Group can attached to the parent gameobject. It makes sure that only one interactor in the group can interact at a time.
- To prevent walking through objects, add Character Controller to XR Origin.
- XR Direct Interactor: allows the user to directly interact with interactables.
- XR Socket Interactor: enables placing interactables into a socket.
- XR Grab Interactable: allows the user to pick up and drop a gameobject, as well as throw or it into a socket.
- XR Simple Interactor: the simplest interactable object that doesn’t really do anything. Hover, select and activate events that programmers can attach their code to.
- You can create your own interactors by inheriting from
BaseInteractor or BaseControllerInteractor.
- You can crate your own interactables by inheriting from
BaseInteractable.
- Interaction Layer Mask: mechanism for filtering which interfactors and interactables can work together.
- Raycast Mask: specifies the physics layers that a raycast can hit.
- Interaction Layer Mask: specifies the interaction layers through which an interactor and interactable can interact.
- Interaction states: Hover -> Select -> Activate
- XR Poke Interactor: allows the user to interact with interactables and UI by poking/touching them.





